Genetic Thought/Memory, and Connectomics/Genomics AI
If a living cell knows what to do in an environment and does it, or adjusts when it can’t, there is something in that cell that plays the role of a form of thought [writer or expression], emerging from a memory [mechanism source].
Though replication can be said to be natural to them, but the coordination aligns with a form of decision making by thought about the right moment, spot or location.
What represents a form of thought in a living cell, and the memory?
Cells have a nucleus where their genetic material is, so where else may thought come from? A reason it is important to look from the thought/memory perspective is because of the number of foreign cells that cause harm to the body. If they can forget what to do, or lose their ability to have a form of thought, it may be easier to fight more diseases.
Advances in medical science makes certain inhibition possible for some cells, however, the specific point where thought could come from, as well as where a form of memory is stored holds new promise for genomics.
The memory supplies menu consistently to genes. Genes have an operational aspect resembling the memory.
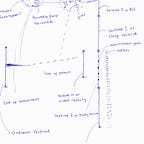
Mapping the brain would lead to new information, but the most important path to seek is thought or a form of thought.
How does thought transport in the brain? Where does it go? Why? What does it activate? What are its types, length and strength? What does destination of thought determine — with what to feel?
That senses are integrated is not new, but to safely theorize that they are integrated to thought is an important step. It is not necessarily about senses, feelings or reaction, it is the thought equivalent of what is sensed, then where they go to give feeling, and reaction.
Without thought going to where emotions are, emotions would not be felt. Thought converted from senses could go there. Those from the memory, or say internal, could as well.
What rules thought follow in the brain are far more applicable than much more — for neurons, whose anatomy and physiology are widely known.
What thoughts are to the mind is different from what neuroimaging shows. Thought forms are numerous, but thought are what senses or signals become to be relayed to the cerebral cortex, amygdala, and so on.
Knowing how thoughts transport would change mental health, approaches to geriatric diseases, and data simulation of thought for emotions in artificial intelligence.