Member-only story
Spring Data JPA: EntityManager Explained!
Understanding EntityManager, Entity, Persistence Context
Published in
4 min readMay 5, 2023
Introduction
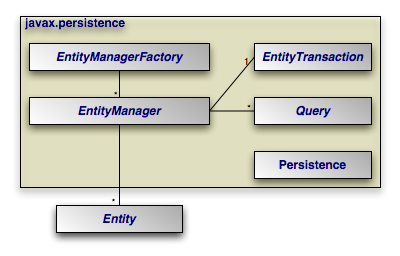
EntityManageris one of the key abstractions that JPA specification defines. EntityManager sits between the database and the application and plays the responsibility of managing the entity in context.- In this article, we will explore these responsibilities and try to learn about EntityManager.
JPA Architecture
Entity
- An Entity is basically a table representation of a relational database and an instance of that entity corresponds to a row in that table.
- It's a domain object in a persistent context.
Example of an Entity
@Entityis an annotation that we use to mark a POJO to the persistent context-aware entity.- @Table allows us to map entities to any custom-named database.
- Other such annotations are @Id @SequenceGenerator @Column etc. that can be used inside the entity.
@Entity
@Table(name="ACCOUNTS")
public class Account {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.SEQUENCE, generator = "accounts_seq")
@SequenceGenerator(name = "accounts_seq", sequenceName = "accounts_seq", allocationSize = 1)
@Column(name = "user_id")
private int userId;
private String username;
private String password;
private String email;
private Timestamp createdOn;
private Timestamp lastLogin;
}Managing Entity
- Entities live in a persistent context (i.e. data store) and the persistent context defines the scope in which entity lifecycle such as creation, updation, removal, etc happens.
- In order to manage the lifecycle of the entity, the EntityManager instance is used. EntityManager instance provides methods using which we can interact with persistent context.
- Persistent Contexts where the entity & entitymanager lives are of two types, which are container-managed and application managed.
Container Managed
- The container-managed persistent context will make sure that…

