Statistical Power
Power is in the context of Statistical Testing, stands for a conditional probability of _REJECTING a FALSE HYPOTHESIS_.
“power -> power of justice -> ability to remove the bad one”

Truth World & Lies World
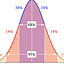
Note that, the Power is a Conditional Probability, on the condition of False null hypothesis.
That being said, the distribution is NOT built on the
null hypothesis is trueanymore, but on thenull hypothesis is false.

How to increase Power
Power is the likelihood that our sample result leads us to correctly reject a false null hypothesis.
The main purpose of studying the power is to get more chance to do the RIGHT thing.
There’re two main settings affect the power of a significance test:
- Significance level: positive impact
- Sample size: positive impact

Impact of Significance Level ⍺
- Higher ⍺ -> Higher Power & Type I Error -> Lower Type II Error
- Lower ⍺ -> Lower Power & Type I Error -> Higher Type II Error
The logic is:
- Lower ⍺ -> closer -> smaller “reject region” -> less chance to reject
- Higher ⍺ -> farther -> larger “reject region” -> more chance to reject

Impact of Sample Size
Larger sample sizes increase power.
Example

Solve:
- To increase power, we want to increase the Significance Level & Sample size as much as possible.
Example

Solve:
- To decrease the Type I Error, we want to decrease the Significance Level & Sample size as much as possible.